Basics of Electricity
To understand EV charging, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental principles of electricity, including voltage, current, and power.

Alternating Current (AC) vs Direct Current (DC)
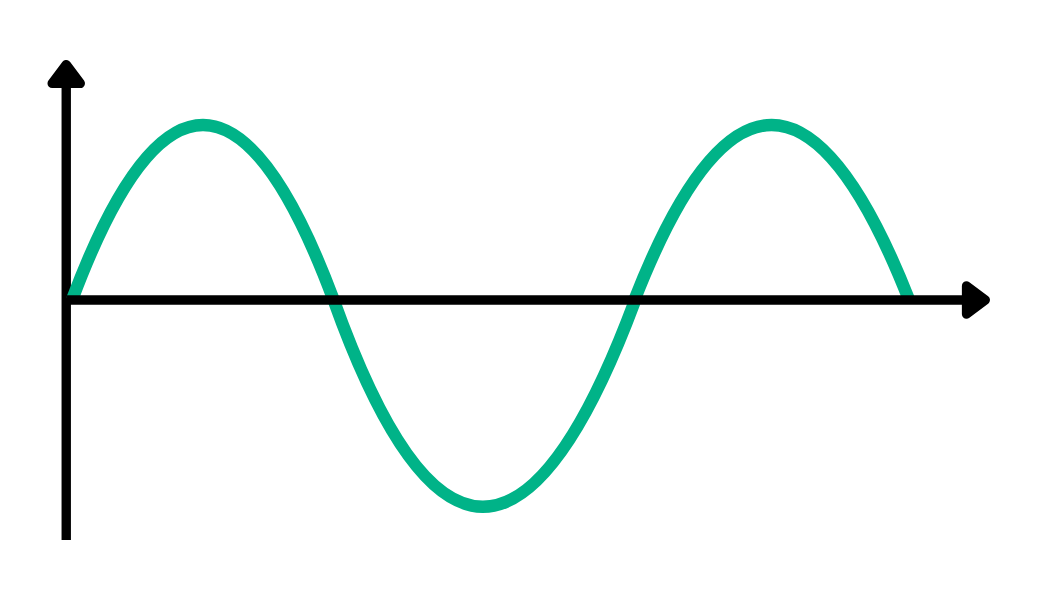
Alternating Current (AC)
AC is the type of electric current that alternates in flow and is generated by the vast majority of power plants and used by most power distribution systems to bring energy to homes and businesses.
Many household appliances use AC electricity. Some electronic devices such as laptops have converters that convert the AC electricity to DC electricity in order to operate the equipment.
Real Life Examples:
Charging your phone
Turning on your TV
Most household appliances

Direct Current (DC)
Direct current is a constant and unidirectional flow of electricity power.
Batteries store energy as direct current, also known as DC energy, which is what a car battery runs on. It provides a stable and consistent power output necessary for starting the engine and running the vehicle's electronic systems. The onboard charger, which is built in an Electrical Vehicle, handles this by converting the AC power into DC energy so that it can be stored in the battery.
Real Life Examples:
Electric & hybrid vehicles
Batteries in a flashlight
Solar panels

Kilowatts (Kw)
A unit of measurement for the rate at which power is used or produced. A watt (W) measures the rate at which energy is produced or consumed. 1000 watts is called a kilowatt (kW).
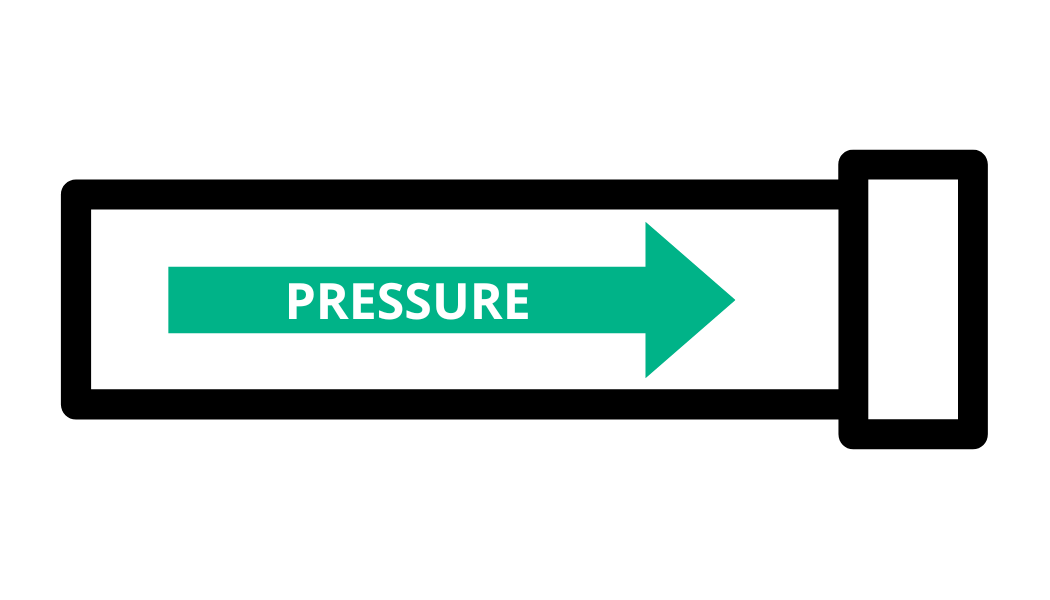
Voltage
(Volts (V))
Voltage is a measurement of the electric potential or "pressure" at which electricity flows through a system. Higher volts means more power.
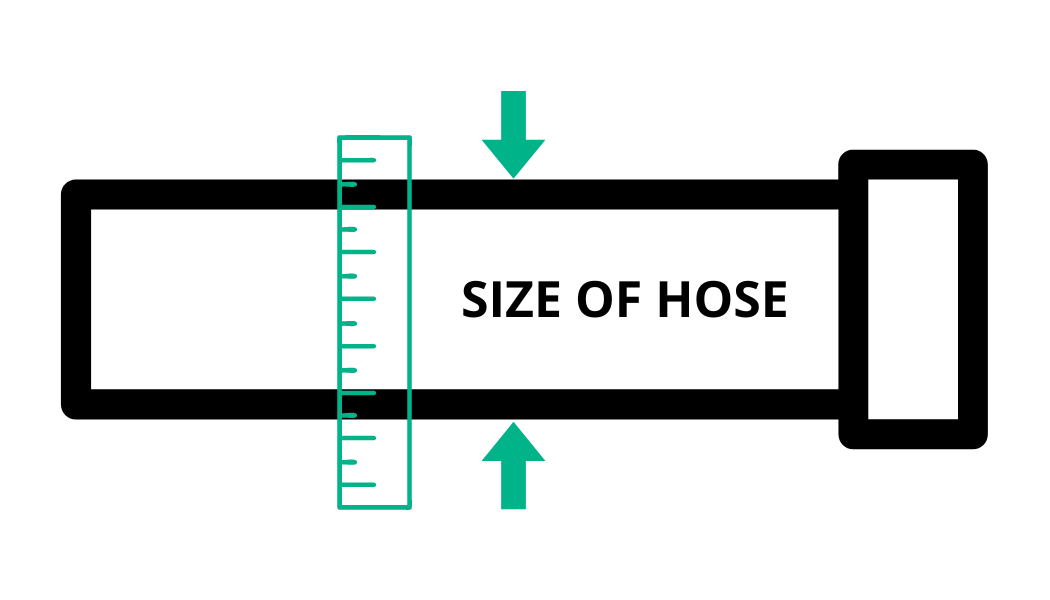
Amperage
(Amps (A or I))
Amperage is the "rate" that the electrical energy current is flowing through a circuit to power equipment. Higher AMPs mean higher power flow.
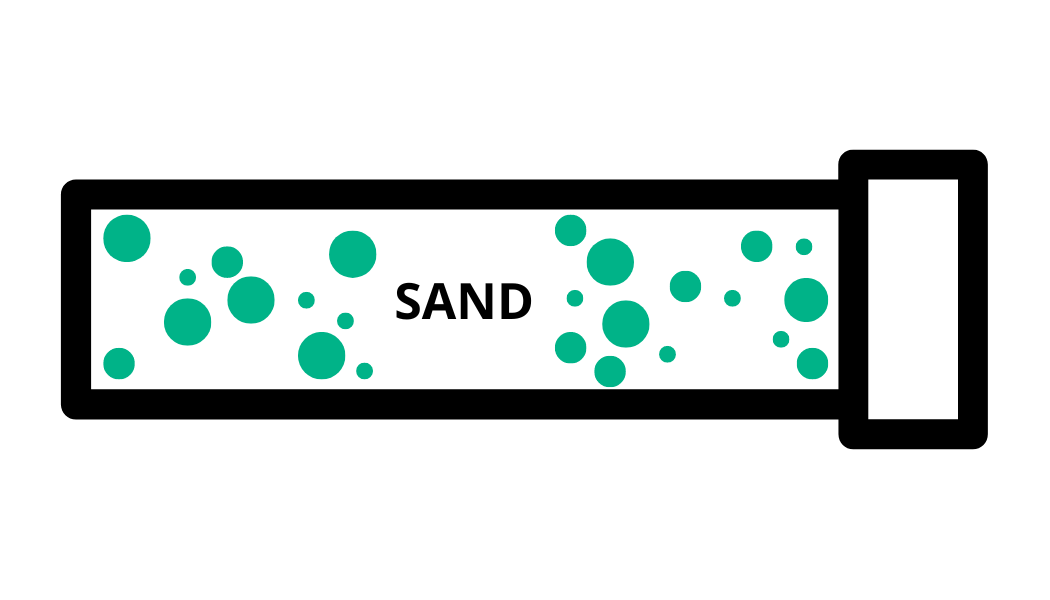
Ohms (R or Ω)
Electrical wires are made of materials that have natural resistance or friction, which slows down the flow of electricity. This resistance is measured in Ohms.
More questions? Let's chat!
Contact Free2move eSolutions anywhere, anytime at +1 (833) 32-CHARGE or supportf2m@f2m-esolutions.com.
